Mybatis(一)主要组件
在实际工作中,已经不止一次的使用Mybatis这个持久化框架,包括逆向工程,XML配置,注解配置,动态SQL,分页或分页插件,与Spring搭配使用,都有过实战操作,但是对理论性知识不够完善,但不够系统化,因此此Mybatis系列诞生。测试使用的Mybatis是3.4.1版本。
一、Mybatis 简介。
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持自定义 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis 免除了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码以及设置参数和获取结果集的工作。MyBatis 可以通过简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原始类型、接口和 Java POJO(Plain Old Java Objects,普通老式 Java 对象)为数据库中的记录。
二、MyBatis 的基本构成
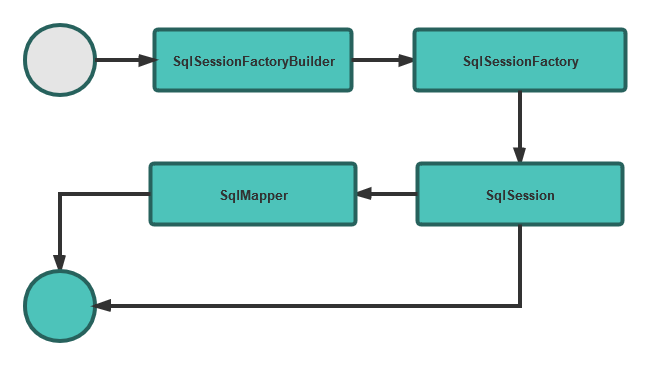
Mybatis核心组件:
- SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(构造器):根据配置信息或代码生成SqlSessionFactory工厂接口。
- SqlSessionFactory(工厂接口):用来生成SqlSession会话。
- SqlSession(会话):是一个可以发送SQL去执行并返回结果、可以获取Mapper的接口。
- SqlMapper:Mybatis新设计的组件,是由一个Java接口和XML文件(或注解)构成,需要给出对应的SQL和映射规则。主要负责发送SQL执行并返回结果。
1、构建SqlSessionFactoy
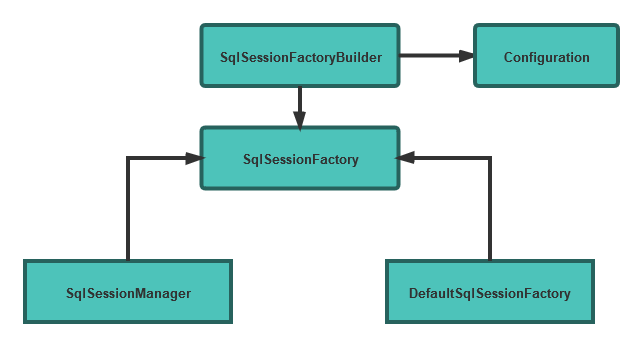
Mybatis应用以SqlSessionFactory的实例为中心,SqlSessionFactory通过SqlSessionFactoryBuider获取。最终是为了创建SqlSession。SqlSession类似Jdbc的连接对象Connection。
但SqlSessionFactory是工厂接口,不能直接创建。Mybatis有两种方式创建SqlSessionFactory:
(A)使用XML配置的方式。
(B)代码方式。
Configuration的类全限定名:org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration.在Mybatis中以一个Configuration类对象的形式存在,生命周期是整个Mybatis应用的生命周期。Mybatis应用解析一次配置的XML会保存到Configuration类对象中,可以重复读取使用。
SqlSession实现类有2个:DefaultSqlSessionFactory 和 SqlSessionManager (暂未使用),如下图:
1、使用XML方式构建
这里以我前几年的一个项目的mybatis-config.xml为例,如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
<!-- 打印查询语句 -->
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING" />
</settings>
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.ssm.web.demo.entity"/>
</typeAliases>
<!-- 数据库连接池信息 -->
<plugins>
<!-- com.github.pagehelper为PageHelper类所在包名 -->
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor">
<!-- 使用下面的方式配置参数,后面会有所有的参数介绍 -->
<!-- <property name="param1" value="value1"/> -->
<property name="reasonable" value="true"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<!--- mappers等 -->
</configuration> 上面的配置文件中没有连接数据库和Mappers节点,是因为我在spring.xml中配置了c3p0连接池,配置了SqlSessionFactory,并指定了mapperLocations。这里要注意的是<configuration>标签,Mybatis解析程序会将配置文件信息解析到Configuration类对象,接着可以利用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建SqlSessionFactory。
package com.ssm.web.demo.test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
public class SqlSessionFactoryTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
try {
//1、创建XML的文件输入流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//2、利用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder读取XML信息来创建SqlSessionFactory
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}2、使用代码的方式构建
(1)构建Configuration的类对象,注册相关信息。
(2)通过Configurationl类对象,构建SqlSessionFactory。
package com.ssm.web.demo.test;
import org.apache.ibatis.datasource.pooled.PooledDataSource;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.Environment;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.apache.ibatis.transaction.TransactionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.transaction.jdbc.JdbcTransactionFactory;
import com.ssm.web.demo.dao.emp.EmployeeMapper;
import com.ssm.web.demo.entity.emp.Employee;
public class SqlSessionFactoryCodeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//构建数据库连接池
PooledDataSource dataSource = new PooledDataSource();
dataSource.setDriver("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://locahost:3306/test");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("123");
//构建数据库事务
TransactionFactory transactionFactory = new JdbcTransactionFactory();
//创建数据库允许环境
Environment evn = new Environment("dev", transactionFactory, dataSource);
//构建Configuration类对象
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(evn);
//注册别名
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAlias("emp", Employee.class);
//加入映射器
configuration.addMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(configuration);
}
}XML方式和JAVA的方式都的类似的。一般情况下用XML方式,如果需要加入自己的特性可以用Java方式。
2、构建SqlSession
SqlSession是一个接口类,真正内部执行的是Executor类。SqlSession通过SqlSessionFactory获取,主要是注意资源回滚与关闭。如下例:
package com.ssm.web.demo.test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
public class SqlSessionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
}finally {
if(sqlSession!=null){
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
}SqlSession的主要用途:
(1)获取映射器,让映射器通过命名空间(XML头部的namespace)和方法名称(sql标签里的id)定位SQL,发送给数据库执行后返回结果。
(2)通过update/insert/select/delete等方法带上SQL的id来操作XML中配置的SQL;通过commit、rollback方法提交或回滚事务。
3、映射器
映射器是由Java接口和XML文件(或注解)共同组成,对参数、缓存、SQL语句、映射关系的管理器。
主要作用:
(1)定义参数类型。
(2)描述缓存。
(3)描述SQL语句。
(4)定义查询结果和POJO的映射关系。
映射器的实现方式:
(A)通过XML文件方式实现。就是在mybatis-config.xml文件中配置POJO的XML,生成Mapper。
(B)代码方式实现。在Configuration里注册Mapper接口。
映射器是Mybatis的核心内容,最复杂。
1)XML方式实现Mapper示例:
(A)定义Java接口:根据主键ID查询Employee对象。
对应的POJO:
package com.ssm.web.demo.entity.emp;
import javax.validation.constraints.Pattern;
public class Employee implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6654960072154305288L;
private Integer Id;
private String empName;
private String sex;
private String email;
public Employee(){}
public Employee(Integer empId, String empName, String sex, String email,int did) {
super();
this.empId = empId;
this.empName = empName;
this.sex = sex;
this.email = email;
this.did = did;
}
public Department getDepartment() {
return department;
}
public void setDepartment(Department department) {
this.department = department;
}
public Integer getEmpId() {
return empId;
}
public void setEmpId(Integer empId) {
this.empId = empId;
}
public String getEmpName() {
return empName;
}
public void setEmpName(String empName) {
this.empName = empName == null ? null : empName.trim();
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex == null ? null : sex.trim();
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email == null ? null : email.trim();
}
}定义对应接口:
package com.ssm.web.demo.dao.emp;
import java.util.List;
import com.ssm.web.demo.entity.emp.Employee;
public interface EmployeeMapper {
Employee selectByPrimaryKey(Integer empId);
}(2)定义XML映射
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.ssm.web.demo.dao.emp.EmployeeMapper">
<select id="selectByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultType="com.ssm.web.demo.entity.emp.Employee">
select
emp_id as empId, emp_name as empName,email as email
from tbl_emp
where emp_id = #{empId,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</select>
</mapper>(a)这个XML文件通常配置在mybatis-config.xml中,mybatis会为这个配置文件生成映射器。
(b)XML定义了一个命名空间为com.ssm.web.demo.dao.emp.EmployeeMapper的SQL Mapper,这个命名空间和接口全限定名称一致。
(c)用select标签定义一个查询SQL,其id和接口的方法名一致。参数类型parameterType的值为”java.lang.Integer”,也和接口方法参数 类型一致。返回类型resultType,如果没有注册别名需要使用对应POJO的全限定,如代码例,如果注册了POJO的别名直接使用别名即可。
(d)#{empId,jdbcType=INTEGER}为这个条SQL的参数,SQL的列别名与POJO的属性名一致。那么Mybatis会把该SQL语句查询结果自动映射到对应的POJO属性上,这个过程称为自动映射。
如果用SqlSession获取Mapper,代码片段如下:
EmployeeMapper empMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
Employee emp = empMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1);这样就完成了一次查询。
当然也可以使用注解SQL方式,有关注解方式会另外单独整理一篇。
package com.ssm.web.demo.dao.emp;
import java.util.List;
import com.ssm.web.demo.entity.emp.Employee;
public interface EmployeeMapper2 {
@Select(value="select emp_id as empId, emp_name as empName,email as email from tbl_emp where emp_id = #{empId}")
Employee selectByPrimaryKey(Integer empId);
}特别注意:
Mybatis依旧可以使用ibatis中通过命名空间和SQL的id,定位执行SQL返回数据的方式,不需要映射器。
Employee emp2 = sqlSession.selectOne("com.ssm.web.demo.dao.emp.DepartmentMapper.selectByPrimaryKey", 1);如果SQL的id全局唯一,还可以省略命名空间:
Employee emp2 = sqlSession.selectOne("selectByPrimaryKey", 1);如果SQL的id不是全局唯一,那么该省略命名空间的写法就有问题。
Mybatis的Mapper只是接口,没有实现类,是一种接口编程模式,是通过Java语言的动态代理来实现的。
在Mybatis上下文描述接口,Mybatis会为该接口生成代理类对象,代理对象会根据“接口全路径+方法名”去匹配,找到对应的XML配置或注解中的SQL任务执行并返回结果。
三、Mybaits组件生命周期
1、SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder利用XML或编码获取资源,构建SqlSessionFactory,它可以构建多个SqlSessionFactory。SqlSessionFactoryBuilder只是一个构造器,构造出SqlSessionFactory之后,作用就完结,会被废弃回收。
作用:作为构造器生成SqlSessionFactory。
生命周期:只存在于方法的局部。
2、SqlSessionFactory
作用:SqlSessionFactory的责任唯一,就是创建SqlSession会话。适合采用单例模式。避免数据库连接资源消耗。
生命周期:Mybatis应用的整个生命周期中。
3、SqlSession
作用:数据库连接会话,相当于JDBC的Connectiond对象。
生命周期:请求数据库处理事务的过程中,可以执行多条SQL保证事务一致性。
是一个线程不安全对象,多线程时需要注册隔离级别和数据库锁等高级特性。
注意SqlSession使用的开启与及时关闭。
4、Mapper
只是一个接口,没有实现类。
作用:发送SQL返回结果或执行SQL修改数据。
生命周期:在SqlSession事务方法内,是方法级别。
相关文章:
| 文章名称 |
|---|
| 《Mybatis(一)主要组件》 |
| 《Mybatis(二)配置》 |
| 《Mybatis(三)动态SQL》 |
| 《Mybtis(四)工作原理》 |
| 《Mybtis(五)Mapper映射器》 |
| 《Mybtis(六)Mapper级联》 |