SpringBoot Cache
一、Jcache
Jcache (JSR107) 是Java体系缓存规范
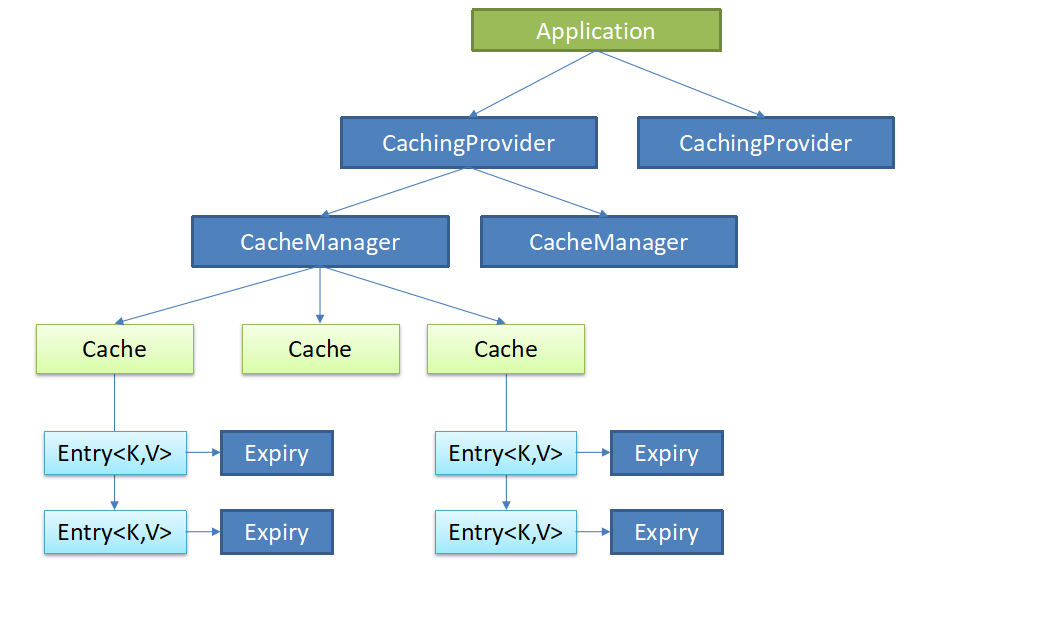
Java Caching定义了5个核心接口,分别是CachingProvider, CacheManager, Cache, Entry 和 Expiry。
CachingProvider定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager。一个应用可以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。
CacheManager定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,这些Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅被一个CachingProvider所拥有。
Cache是一个类似Map的数据结构并临时存储以Key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个CacheManager所拥有。
Entry是一个存储在Cache中的key-value对。
Expiry 每一个存储在Cache中的条目有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置
基本包 cache-api-x.x.x.jar
二、Spring Cache
1、主要内容
Spring 3.1 也有了缓存支持,称为抽象缓存,也支持使用 Jcache 注解。
Spring 的 Cache 在 spring-context 包中。
两个重要接口:
org.springframework.cache.Cache: Cache 接口为缓存组件规范定义,包含各种常见的缓存操作。spring在缓存接口下提供了各种XxxCache 的实现,如操作redis的 RedisCache、还有EhCacheCache、ConcurrentMapCache 等。org.springframework.cache.CacheManager: 缓存管理器,管理各种缓存组件。CacheManager 管理多个Cache组件,对缓存的真正CURD操作在Cache组件中,每个一缓存组件都有自己唯一的名字。
缓存使用过程:
当调用需要缓存功能的方法时,spring 会检查目标方法(参数)是否已经被调用过,如果调用过就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用目标方法并缓存结果后返回,下次调用直接从缓存获取。
Spring 缓存抽象关注点:
- 确定方法需要被缓存以及缓存数据的策略
- 从缓存中读取之前已缓存数据。
重要的缓存注解:
**@EnableCaching**: 开启基于注解的缓存使用。**@Cacheable**: 主要是针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对返回结果进行缓存。适合select操作。**@CacheEvict**: 清空缓存。适合delete操作。**@CachePut**: 保证方法被调用、又希望结果被缓存。 适合update操作。**@CacheConfig**:类注解,全类生效的公共配置。
重要注解参数:
keyGenerator : 缓存数据时 key 生成策略。
serialize: 缓存数据时 value 序列号策略。
2、SpringBoot 默认Cache:
1、自动配置类
在 SpringBoot 中使用org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration 进行自动配置。
2、缓存配置类
缓存配置类可以在spring-boot-autoconfigure 包的org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache 路径下看的:
(注意:这是spring-boot-2.2.10版本的)
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CaffeineCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CouchbaseCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.EhCacheCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GenericCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.HazelcastCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.InfinispanCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.JCacheCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.NoOpCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration默认使用SimpleCacheConfiguration 。(debug=true)
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheManager;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({CacheManager.class})
@Conditional({CacheCondition.class})
class SimpleCacheConfiguration {
SimpleCacheConfiguration() {
}
@Bean
ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager(CacheProperties cacheProperties, CacheManagerCustomizers cacheManagerCustomizers) {
//new 创建的 ConcurrentMapCacheManager 缓存管理器
ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager = new ConcurrentMapCacheManager();
List<String> cacheNames = cacheProperties.getCacheNames();
if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) {
cacheManager.setCacheNames(cacheNames);
}
return (ConcurrentMapCacheManager)cacheManagerCustomizers.customize(cacheManager);
}
}在容器中创建了一个缓存管理器:ConcurrentMapCacheManager ,这个缓存管理器可以获取和创建ConcurrentMapCache 源码如下:
package org.springframework.cache.concurrent;
public class ConcurrentMapCacheManager implements CacheManager, BeanClassLoaderAware {
private final ConcurrentMap<String, Cache> cacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap(16);
private boolean dynamic = true;
private boolean allowNullValues = true;
private boolean storeByValue = false;
@Nullable
private SerializationDelegate serialization;
public ConcurrentMapCacheManager() {
}
public ConcurrentMapCacheManager(String... cacheNames) {
this.setCacheNames(Arrays.asList(cacheNames));
}
public void setCacheNames(@Nullable Collection<String> cacheNames) {
if (cacheNames != null) {
Iterator var2 = cacheNames.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
String name = (String)var2.next();
this.cacheMap.put(name, this.createConcurrentMapCache(name));
}
this.dynamic = false;
} else {
this.dynamic = true;
}
}
public Collection<String> getCacheNames() {
return Collections.unmodifiableSet(this.cacheMap.keySet());
}
// 根据名字获取对应的缓存组件
@Nullable
public Cache getCache(String name) {
Cache cache = (Cache)this.cacheMap.get(name);
if (cache == null && this.dynamic) {
synchronized(this.cacheMap) {
cache = (Cache)this.cacheMap.get(name);
if (cache == null) {
cache = this.createConcurrentMapCache(name);
this.cacheMap.put(name, cache);
}
}
}
return cache;
}
// 创建缓存管理器
protected Cache createConcurrentMapCache(String name) {
SerializationDelegate actualSerialization = this.isStoreByValue() ? this.serialization : null;
return new ConcurrentMapCache(name, new ConcurrentHashMap(256), this.isAllowNullValues(), actualSerialization);
}
}3、@Cacheable
@Cacheable 将方法运行的结果进行缓存,以后要查询相同数据,可以直接从缓存获取,不调用方法。在缓存失效之前掉一次,确保缓存存在。boot中的源码:
package org.springframework.cache.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Cacheable {
@AliasFor("cacheNames")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] cacheNames() default {};
String key() default "";
String keyGenerator() default "";
String cacheManager() default "";
String cacheResolver() default "";
String condition() default "";
String unless() default "";
boolean sync() default false;
}3.1 相关参数:
value / cacheNames: 缓存组件的名字。String[]数组可以指定多个。key: 缓存数据时使用的key,可以自定义。默认是使用方法参数的值。 key的值支持SpEL格式:#id参数id的值,#a0,#p0,#root.args[0]等。keyGenerator: key的生成器,可以自己指定自己的key生成器的组件id。keyGenerator 和 key 二选一即可cacheManager: 指定缓存管理器,表示从哪个缓存管理器获取缓存。cacheResolver:指定缓存解析器。与cacheManager相同,二选一使用即可。condition: 条件满足则进行缓存unless:除非当unless 指定的条件为true,方法的返回值就不缓存。可以获取结果进行判断。 如:结果为null时不使用缓存unless = "#result==null"sync: 是否使用异步模式。
3.2 Cache SpEL 支持
| 名字 | 位置 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| methodName | root object | 当前被调用的方法名 | #root.methodName |
| method | root object | 当前被调用的方法 | #root.method |
| target | root object | 当前被调用的目标对象 | #root.target |
| targetClass | root object | 当前被调用的目标对象类 | #root.targetClass |
| args | root object | 当前被调用的方法的参数列表 | #root.args[0] |
| caches | root object | 当前方法调用使用的缓存列表 如 @Cacheable(value={“cache1”,”cache2”}),表示有两个cache可以缓存返回结果。 | #root.caches[0].name |
| argument name | evaluation context | 方法参数的名字,可以直接 #参数名,也可以使用 #p0或#a0的形式,0表示参数索引。 | #param、#a0、#p1 |
| result | evaluation context | 方法执行后的返回值。方法执行后判断有效才可以,如unless/cache put 的表达式 cache evict的表达式 beforeInvocation=false) | #result |
3.1 工作运行流程
(1)在方法运行之前,CacheManager (缓存管理器)先会按照cacheName 指定的名字,去查找获取Cache(缓存组件),第一次获取缓存没有,Cache组件会自动创建。
(2)使用缓存的key(默认是方法参数)去Cache (缓存组件)中查找缓存的容器。 Key是按照某种策略生成,默认使用keyGenerator生成,默认使用SimpleKeyGenerator 生成Key。
- SimpleKeyGenerator 的默认策略:
- 如果没有参数:key = new SimpleKey();
- 如果有一个参数:key=参数值;
- 如果有多个参数:key=new Simple(params)。
(3)没有查到缓存数据就会调用目标方法。
(4)将目标的结果put操作放入缓存(ConcurrentMap)中。
3.2 原理小结
(1)使用CacheManager 【实际类名为ConcurrentMapCacheManager】按照缓存组件名得到缓存组件Cahe【实际类名为ConcurrentMapCache】
(2)key使用的是KeyGenerator生成的,默认是SimpleKeyGenerator。
(3)@Cacheable 标注的方法执行前先检查缓存中是否已有该数据,默认按照参数的值作为key去查询缓存,如果没有就运行方法并将结果放入缓存,后续可以直接使用缓存数据。
3.3 主要属性
(1)key的使用
配合SpEL使用即可。示例:
@Cacheable(value={"user"},key="#id")
public User getUseById(Integer id){
} 或者自动组装
示例1:@Cacheable(value={"user"},key="#root.method +'['+ #id + ']'")
示例2:@Cacheable(value={"user"},key="'user_'+ #id + ']'")
@Cacheable(value={"user"},key="'user_'+ #id + ']'")
public User getUseById(Integer id){
} (2)keyGenerator 使用:
自定义一个生成key的配置类:
@Configuration
public class UseCacheConfig {
@Bean
public KeyGenerator userkeyGenerator(){
return new KeyGenerator() {
@Override
public Object generate(Object o, Method method, Object... objects) {
return method.getName()+"["+ Arrays.asList(objects).toString()+"]";
}
};
}
}Lambda 写法:参数类型也可以省略。
@Bean
public KeyGenerator userkeyGenerator(){
return (Object o, Method method, Object... objects) -> {
return method + "[" + Arrays.asList(objects).toString() + "]";
};
}使用:
@Cacheable(value={"user"},keyGenerator="userkeyGenerator")
public User getUseById(Integer id){
} (2)Condition 使用
@Cacheable(value={"user"},keyGenerator="userkeyGenerator",condition="#a0 > 0 and #root.methoed equles 'getUseById'")
public User getUseById(Integer id){
} id 值大于 0 才缓存
(3)unless 使用
@Cacheable(value={"user"},keyGenerator="userkeyGenerator",condition="#a0>0",unless="#id == 0")
public User getUseById(Integer id){
} id 值为0 的查询结果不缓存。
4、@CachePut
既要调用方法,又要更新缓存数据。
使用场景:修改了数据库的某(个)些数据,同时更新缓存。
运行流程:
(1)先调用目标方法
(2)将目标方法的结果缓存起来
示例:
@CachePut(value="user",key="#result.id")
public User updateUser(User user){
} key="#result.id" 或 key="#user.id" 效果相同。
前面的查询使用的key是key="#id",此处也要是key="#user.id 。
前面的查询使用的key是key="'user_'+ #id + ']'",则此处也要是key="'user_' + #user.id + ']'" 。
注意事项:若想让数据修改之后更新缓存,则必须使用相同key的缓存数据,如果key不一致,无法更新前面查询结果缓存。
测试思路:
1、先查询某个结果,确保结果已经在某个缓存组件;
2、测试更新操作,缓存组件要与查询的缓存组件相同;
3、再次查询之前已缓存结果;
4、如过拿到的缓存结果未更新,检查key是否一致;
5、如过拿到的缓存结果更新,说明注解生效。
5、@CacheEvict
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.cache.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface CacheEvict {
@AliasFor("cacheNames")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] cacheNames() default {};
String key() default "";
String keyGenerator() default "";
String cacheManager() default "";
String cacheResolver() default "";
String condition() default "";
boolean allEntries() default false;
boolean beforeInvocation() default false;
}@CacheEvict缓存清楚,如果删除了某个数据,缓存要对应删除。
allEntries 属性可以清除缓存所有数据,默认是false,设置为true,则会清除缓存组件里所有数据。
beforeInvocation 是否在方法之前执行。默认是false,表示在方法之后执行,方法出错时则不会清除缓存数据。设置beforeInvocation=true,则表示在方法之前执行,不管方法是否执行成功,缓存都会被清除。
常见示例:
清除指定key的缓存数据:
@CacheEvict(value="user",key="#id")
public boolean deleteUser(Integer id){
// code
return true;
}清除全部的缓存数据:
@CacheEvict(value="user",allEntries=true)
public boolean deleteUser(Integer id){
// code
return true;
}在方法执行之前清除缓存:
@CacheEvict(value="user",beforeInvocation=true)
public boolean deleteUser(Integer id){
// code
int a = 10/0 ;
return true;
}6、@Caching
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.cache.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Caching {
Cacheable[] cacheable() default {};
CachePut[] put() default {};
CacheEvict[] evict() default {};
}从源码中可以看出 @Caching其实就是上面三个的组合使用, 可以指定多个复杂的缓存规则。
示例:
@Caching(
cacheable = {
@Cacheable(value="user",key="#username")
},
put = {
@CachPut(value="user",key="#result.id")
@CachPut(value="user",key="#result.email")
}
)
public User getUserByName(String username){
User user= userdao.getUserByName(username);
return user;
}7、@CacheConfig
package org.springframework.cache.annotation;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface CacheConfig {
String[] cacheNames() default {};
String keyGenerator() default "";
String cacheManager() default "";
String cacheResolver() default "";
}
源代码可以看出这是用在类上的注解,从属性可以看出,其实就是将一些方法上定义的相同的缓存名字,缓存key,缓存管理器抽取出来写成共用配置。
示例
@CacheConfig(value="user")
public class UserService{
//code
}三、SpringBoot Redis Cache
前面学习了SpringBoot默认Cache是利用ConcurrentMapCacheManager缓存管理器来管理默认的缓存组件ConcurrentMapCache。
1、环境准备:
(1)使用云服务器安装redis,或者使用 VM 安装redis,或者使用 docker 安装redis
(2)springboot 使用redis 需要引入redis的starter:spring-boot-starter-data-redis 使得RedisAutoConfiguration 生效,容器中添加SpringRedisTemplate 和RedisTemplate操作对象。
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis;
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@ConditionalOnClass({RedisOperations.class})
@EnableConfigurationProperties({RedisProperties.class})
@Import({LettuceConnectionConfiguration.class, JedisConnectionConfiguration.class})
public class RedisAutoConfiguration {
public RedisAutoConfiguration() {
}
// 操作K-V 都是Object
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
name = {"redisTemplate"}
)
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
// 操作K-V 都是字符串的
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException {
StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
}并且作为缓存的管理管理器是RedisCacheManager,换组组件是RedisCache。
(3)配置redis的host:
spring.redis.host=192.168.88.82(4)自定义redis存储的序列化器
package com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
/**
* @description: TODO 功能角色说明:
* TODO 描述:
* @author: 张小菜
* @date: 2020/10/25 17:15
* @version: v1.0
*/
@Configuration
public class UseRedisConfig {
// 自定义 操作User 的RedisTemplate
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> useredisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> defaultSz = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
template.setDefaultSerializer(defaultSz);
return template;
}
}(5)Redis环境测试
package com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache;
import com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.model.User;
import com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.service.UserService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith( SpringRunner.class )
@SpringBootTest
class BootCacheApplicationTests {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
@Autowired
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Autowired
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/**
* 测试 Redis 常规操作
* String/List/Set/Hash/Zset
* stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue() 字符串操作
* redisTemplate.opsForList() 列表操作
* redisTemplate.opsForSet() Set集合
* redisTemplate.opsForHash() 散列操作
* redisTemplate.opsForZSet() 有序集合
* redisTemplate.opsForValue() 操作对象
*/
@Test
public void testRedis01() {
String username = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("username");
System.out.println(username);
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("list01","xiao1");
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("list01","cai2");
}
//测试保存对象,注意对象一定要实现序列化接口,默认使用jdk的序列化机制
@Test
public void testRedis02() {
User user = userService.getUserById(1);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("user-01",user);
}
}2、Redis 缓存工作原理
工作原理:
(1)引入redis的starter 之后,容器中创建了RedisCacheManager 来管理缓存组件。
(2)RedisCacheManager 缓存管理器创建了RedisCache 作为缓存组件,RedisCache 通过操作Redis 实现缓存数据。RedisCache 操作redis 时使用的RedisTemplate<Object,Object> 对象。
(3)默认保存数据是K-V都是Object形式,需要理由序列化来保存,如转出json格式。
3、Redis 多缓存管理器
可以模仿 RedisCacheConfiguration 自定义不同业务缓存管理器RedisCacheManager :
package com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.config;
import com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.mapper.Deptment;
import com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.model.User;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheWriter;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import java.time.Duration;
/**
* @description: TODO 功能角色说明: 自定义 Redis 不同业务操作和 不同业务的缓存管理器
* TODO 描述:
* @author: 张小菜
* @date: 2020/10/25 17:15
* @version: v1.0
*/
@Configuration
public class UseRedisConfig {
// 自定义 操作User 的RedisTemplate
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, User> useredisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, User> template = new RedisTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<User> defaultSz = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(User.class);
template.setDefaultSerializer(defaultSz);
return template;
}
// 自定义 操作Deptment 的RedisTemplate
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Deptment> deptRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Deptment> template = new RedisTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Deptment> defaultSz = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Deptment.class);
template.setDefaultSerializer(defaultSz);
return template;
}
// 定制 用户缓存的 Redis 缓存管理器 userRedisCacheManager
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager userCacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
//初始化一个RedisCacheWriter
RedisCacheWriter redisCacheWriter = RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(redisConnectionFactory);
//设置CacheManager的值序列化方式为json序列化
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<User> jsonSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(User.class);
RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair<User> serializationPair = RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(jsonSerializer);
RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfig = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.serializeValuesWith(serializationPair);
//设置默认超过期时间是30秒
defaultCacheConfig.entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(30));
//初始化RedisCacheManager
//默认使用前缀的
return new RedisCacheManager(redisCacheWriter, defaultCacheConfig);
}
// 定制 用户缓存的 Redis 缓存管理器 userRedisCacheManager
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager deptCacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
//初始化一个RedisCacheWriter
RedisCacheWriter redisCacheWriter = RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(redisConnectionFactory);
//设置CacheManager的值序列化方式为json序列化
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Deptment> jsonSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Deptment.class);
RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair<Deptment> serializationPair = RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(jsonSerializer);
RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfig = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.serializeValuesWith(serializationPair);
//设置默认超过期时间是30秒
defaultCacheConfig.entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(30));
//初始化RedisCacheManager
//默认使用前缀的
return new RedisCacheManager(redisCacheWriter, defaultCacheConfig);
}
}在使用的时候就可以根据不同的业务使用不同的redis操作来管理各自的缓存组件。这里可以以管理器区分业务,也可以使用cacheName不同来区分业务。
比如用户业务:
package com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.service;
import com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.model.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @description: TODO 功能角色说明:
* TODO 描述:
* @author: 张小菜
* @date: 2020/10/25 16:59
* @version: v1.0
*/
//缓存管理器写在类上示例(推荐)
@CacheConfig(cacheManager = "userCacheManager")
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
@Cacheable(value = "user",key = "#id")
public User getUserById(int id) {
User user = userMapper.getUserById(id);
return user;
}
}比如部门业务:
package com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.service;
import com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.mapper.DeptMapper;
import com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.model.Deptment;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @description: TODO 功能角色说明:
* TODO 描述:
* @author: 张小菜
* @date: 2020/10/25 16:59
* @version: v1.0
*/
@CacheConfig
@Service
public class DeptService {
@Autowired
private DeptMapper deptMapper;
// 缓存管理器写在方法示例
@Cacheable(value = "dept",key = "#id",cacheManager = "deptCacheManager")
public Deptment getUserById(int id) {
Deptment user = deptMapper.getDeptmentById(id);
return user;
}
}如果要配置统一的前缀也可以参考缓存配置文件 CacheProperties:全路径是:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheProperties
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache;
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.cache")
public class CacheProperties {
}四、编程式缓存操作
尽管已经逐渐走向注解开发,但是编程式的操作的是面向过程了,对于操作流程更直观,方便理解。
使用步骤:
(1)将容器中的缓存管理器注入到相关类中
(2)利用缓存管理器,通过 cacheName 获取对应的cache组件。
(3)使用cache缓存组件操作缓存即可。
1、Spring 抽象缓存操作
将注解和编程写在一起,可以对比理解。
(编程式写法未测试,这样写只是方便理解)
package com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.service;
import com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.mapper.DeptMapper;
import com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.model.Deptment;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.Cache;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheManager;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @description: TODO 功能角色说明:
* TODO 描述:
* @author: 张小菜
* @date: 2020/10/25 16:59
* @version: v1.0
*/
@CacheConfig
@Service
public class DeptService {
@Autowired
private DeptMapper deptMapper;
@Autowired
private ConcurrentMapCacheManager concurrentMapCacheManager;
// 调用方法,结果进行缓存,后续使用缓存
@Cacheable(value = "dept",key = "#id")
public Deptment getDeptmentById(int id) {
Deptment deptment = deptMapper.getDeptmentById(id);
return deptment;
}
// 调用方法,且更新缓存
@CachePut(value="dept",key="#result.id")
public Deptment updateDeptment(Deptment deptment) {
Deptment deptment2 = deptMapper.updateDeptment(deptment);
return deptment2;
}
// 调用方法,清空缓存
@CacheEvict(value="dept",key="#result.id")
public void deleteDeptmentById(int id) {
deptMapper.deleteDeptmentById(id);
}
// 查询
public Deptment getDeptmentByIdTest02(int id) {
// 先从缓存获取
Cache deptCache = concurrentMapCacheManager.getCache("dept");
Deptment deptment = deptCache.get(id, Deptment.class);
if(deptment != null ){
return deptment;
}
// 缓存没有再去查询数据库
deptment= deptMapper.getDeptmentById(id);
deptCache.put("1", deptment);
return deptment;
}
// 更新
public Deptment updateDeptmentTest02(Deptment deptment) {
Deptment deptment2 = deptMapper.updateDeptment(deptment);
// 更新成功后更新缓存
Cache deptCache = concurrentMapCacheManager.getCache("dept");
deptCache.put("1", deptment2);
return deptment2;
}
// 删除
public void deleteDeptmentByIdTest02(int id) {
deptMapper.deleteDeptmentById(id);
// 删除成功后清空缓存
Cache deptCache = concurrentMapCacheManager.getCache("dept");
deptCache.evict(id);
}
}2、Redis 缓存操作
将注解和编程写在一起,可以对比理解。
(编程式写法未测试,这样写只是方便理解)
package com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.service;
import com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.xiaocai.cache.bootcache.model.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.Cache;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @description: TODO 功能角色说明:
* TODO 描述:
* @author: 张小菜
* @date: 2020/10/25 16:59
* @version: v1.0
*/
@CacheConfig(cacheManager = "userCacheManager")
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private RedisCacheManager userCacheManager;
// 调用方法,结果进行缓存,后续使用缓存
@Cacheable(value = "user",key = "#id")
public User getUserById(int id) {
User user = userMapper.getUserById(id);
return user;
}
// 调用方法,且更新缓存
@CachePut(value="user",key="#result.id")
public User updateUser(User user) {
User user2 = userMapper.updateUser(user);
return user2;
}
// 调用方法,清空缓存
@CacheEvict(value="user",key="#result.id")
public void deleteUserById(int id) {
userMapper.deleteUserById(id);
}
// 查询
public User getUserByIdTest02(int id) {
// 先从缓存获取
Cache userCache = userCacheManager.getCache("user");
User user = userCache.get(id, User.class);
if(user != null ){
return user;
}
// 缓存没有再去查询数据库
user = userMapper.getUserById(id);
userCache.put("1", user);
return user;
}
// 更新
public User updateUserTest02(User user) {
User user2 = userMapper.updateUser(user);
// 更新成功后更新缓存
Cache userCache = userCacheManager.getCache("user");
userCache.put("1", user);
return user2;
}
// 删除
public void deleteUserByIdTest02(int id) {
userMapper.deleteUserById(id);
// 删除成功后清空缓存
Cache userCache = userCacheManager.getCache("user");
userCache.evict(id);
}
}很容易看出二者差别不大,就是各自的缓存管理器和缓存组件不一样,用法基本上都遵循Cache相关接口规范。
如果换了一个缓存组件,道理相同。
学习参考尚硅谷学习视频